Flatbed For Trucks Blueprints: Your Comprehensive Guide to Custom Hauling Solutions
Flatbed For Trucks Blueprints: Your Comprehensive Guide to Custom Hauling Solutions cars.truckstrend.com
Introduction: The Foundation of Custom Hauling
In the world of trucking, versatility and functionality are paramount. While factory-standard truck beds serve many purposes, they often fall short when specific hauling needs arise. This is where Flatbed For Trucks Blueprints emerge as an invaluable resource. Far more than just drawings, these blueprints are detailed engineering plans that provide the precise specifications, dimensions, and material requirements needed to construct a custom flatbed. Whether you’re a professional fabricator, a DIY enthusiast, or a business owner looking to optimize your fleet, understanding and utilizing flatbed blueprints empowers you to create a hauling solution perfectly tailored to your unique demands.
Flatbed For Trucks Blueprints: Your Comprehensive Guide to Custom Hauling Solutions
From heavy equipment transport to specialized cargo and even mobile workshops, a custom flatbed offers unparalleled adaptability. Blueprints democratize this customization process, allowing individuals and companies to either build their own flatbeds from scratch, modify existing designs, or commission professional fabricators with clear, precise instructions. This article will delve into the intricacies of flatbed truck blueprints, exploring their components, benefits, design considerations, and practical advice to help you embark on your custom flatbed journey.
What Exactly Are Flatbed Truck Blueprints?
At its core, a flatbed truck blueprint is a detailed technical drawing or set of drawings that outlines every aspect of a flatbed design. Think of it as the architectural plan for your truck bed. These comprehensive documents typically include:
- Dimensional Drawings: Precise measurements for length, width, height, and clearances, ensuring compatibility with specific truck chassis models.
- Material Specifications: Recommended types and gauges of steel, aluminum, wood, or composite materials for the frame, deck, and structural components, often including specific alloys.
- Structural Details: Cross-sectional views, beam sizes, gusset plate designs, and reinforcement points critical for strength and load-bearing capacity.
- Welding and Fastening Schedules: Detailed instructions on joint types, weld sizes, bolt patterns, and fastener specifications to ensure structural integrity and safety.
- Mounting System Details: How the flatbed attaches to the truck’s frame, including mounting brackets, bolt hole patterns, and anti-vibration measures.
- Accessory Integration: Plans for headache racks, stake pockets, tie-down points, underbody toolboxes, lighting cutouts, and other integrated features.
- Wiring Diagrams: For integrated lighting, auxiliary power, and other electrical components, ensuring compliance with road safety regulations.
- Weight Distribution and Load Capacity Calculations: Although sometimes separate, good blueprints often provide guidelines for these critical safety aspects.
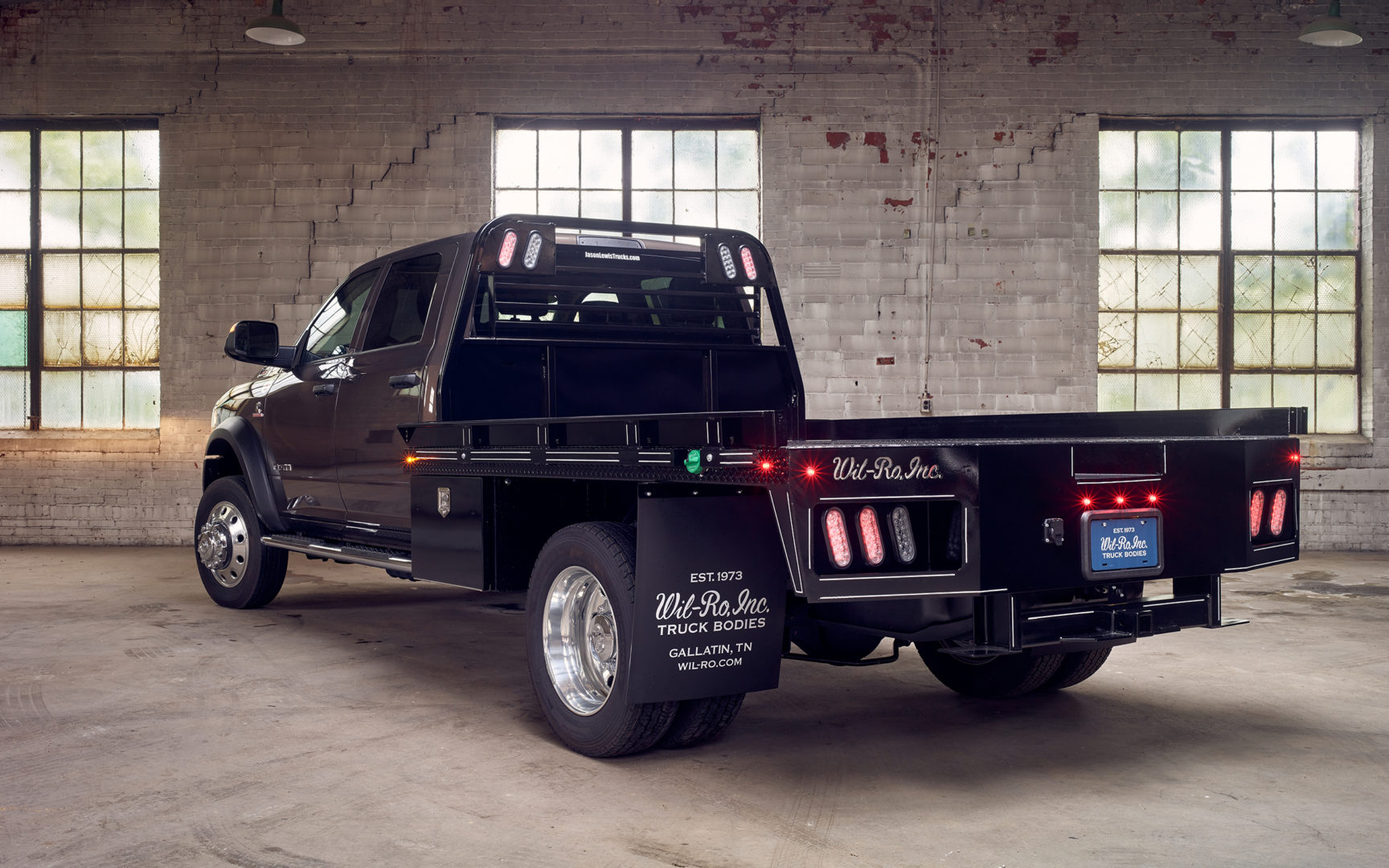


These blueprints transform a conceptual idea into a tangible, buildable project, serving as the definitive guide for construction.
Why Opt for Flatbed Blueprints? The Undeniable Advantages
Choosing to build or commission a flatbed based on detailed blueprints offers a multitude of benefits over purchasing a generic, off-the-shelf option:
- Unmatched Customization: This is the primary driver. Blueprints allow you to design a flatbed that perfectly matches your cargo type, size, weight, and specific operational needs. Need extra-long, wider, or with specific tie-down configurations? Blueprints make it possible.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While initial blueprint costs might exist for custom designs, building a flatbed from plans can often be more economical than buying a specialized factory unit, especially if you have fabrication skills or access to affordable labor. You control material choices and features.
- Optimized Performance: A custom flatbed can be engineered for optimal weight distribution, maximizing payload capacity while staying within legal GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating) limits.
- Durability and Longevity: By selecting specific materials and reinforcing critical areas based on your intended use, a custom-built flatbed can often surpass the durability of mass-produced alternatives.
- Repairability and Modularity: Having the original blueprints makes future repairs, modifications, or additions much simpler, as all structural details are readily available.
- Learning and Skill Development: For DIY enthusiasts, following blueprints provides an invaluable hands-on learning experience in metal fabrication, welding, and automotive mechanics.
- Specific Industry Needs: Industries like logging, construction, agriculture, or mobile service often require highly specialized flatbeds that only custom blueprints can deliver.

Key Components of a Flatbed Design
Understanding the anatomy of a flatbed is crucial before delving into design:
- Main Frame Rails: The primary longitudinal beams that run the length of the flatbed, providing its core strength and attaching to the truck’s chassis.
- Crossmembers: Transverse beams that connect the main frame rails, supporting the deck and distributing weight.
- Decking: The flat surface of the bed, typically made from wood (like treated lumber or oak), steel, or aluminum, on which cargo rests.
- Headache Rack: The vertical structure behind the cab, protecting the cab and occupants from shifting cargo and often incorporating lights or tool storage.
- Stake Pockets & Side Rails: Slots around the perimeter for inserting removable stakes or side panels, offering cargo containment flexibility.
- Tie-Down Points: D-rings, rub rails, or winch tracks strategically placed for securing cargo safely.
- Lighting: Integrated LED tail lights, brake lights, turn signals, and marker lights for DOT compliance.
- Mounting System: Brackets, bolts, and shims that securely fasten the flatbed to the truck’s frame, allowing for chassis flex.
- Underbody Toolboxes: Optional storage compartments mounted beneath the deck for tools and equipment.
Materials Selection for Your Flatbed
The choice of material significantly impacts the flatbed’s weight, strength, cost, and maintenance. Blueprints will specify these, but it’s good to understand the options:
- Steel (Mild Steel, High-Strength Steel):
- Pros: Extremely strong, durable, relatively inexpensive, easy to weld.
- Cons: Heavy (reduces payload capacity), susceptible to rust (requires painting/coating).
- Best For: Heavy-duty applications, maximizing strength where weight isn’t the absolute primary concern.
- Aluminum (6061-T6, 5052):
- Pros: Lightweight (maximizes payload), corrosion-resistant, good aesthetics.
- Cons: More expensive than steel, harder to weld (requires specialized techniques), less impact resistant than steel.
- Best For: Maximizing fuel efficiency, lighter loads, or applications where rust is a major concern (e.g., coastal areas).
- Wood (Oak, Treated Pine, Composite):
- Pros: Relatively inexpensive for decking, easy to replace, good friction for cargo.
- Cons: Less durable than metal, susceptible to rot and wear, requires more maintenance.
- Best For: Decking material where a "softer" surface is preferred or for traditional aesthetics.
- Composites:
- Pros: Very lightweight, strong, corrosion-resistant.
- Cons: Very expensive, specialized fabrication required.
- Best For: Niche, high-performance applications where budget is less of a concern.
Designing Your Flatbed: A Step-by-Step Guide
Whether you’re drawing your own or commissioning a designer, the process follows a logical flow:
-
Define Your Needs:
- Truck Type: What is the make, model, year, and wheelbase of your truck? (Critical for frame compatibility).
- Primary Use: What will you be hauling? How much does it weigh? What dimensions does it have?
- Desired Features: Headache rack, gooseneck hitch, removable sides, toolboxes, crane mounts, etc.
- Budget: This will influence material choices and professional help.
-
Research & Inspiration: Look at existing flatbeds, both custom and factory. Gather ideas for features, aesthetics, and structural approaches. Understand local and national regulations (DOT, GVWR).
-
Conceptual Sketching: Begin with rough hand sketches. Don’t worry about precision yet, just get your ideas down. Experiment with different layouts and features.
-
Detailed Blueprints (Manual or CAD):
- Manual Drafting: For simpler designs, clear, precise hand drawings with accurate measurements and views (top, side, front, rear, isometric) can suffice.
- CAD Software (Computer-Aided Design): For complex designs, CAD programs (like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Fusion 360) are invaluable. They allow for precise measurements, 3D modeling, stress analysis, and easy modifications. Many professional blueprint sets are generated this way.
-
Material Sourcing: Based on your blueprints, create a detailed bill of materials. Obtain quotes from suppliers for steel, aluminum, decking, fasteners, and other components.
-
Fabrication & Welding (If DIY):
- Safety First: Always wear appropriate PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) – welding helmet, gloves, fire-resistant clothing.
- Tools: You’ll need a welder (MIG, TIG, or Stick), grinder, cut-off tools, clamps, measuring tools, and a level.
- Precision: Follow the blueprints meticulously. Measure twice, cut once. Ensure squareness and plumbness at every step.
- Welding Quality: Strong, clean welds are paramount for safety and durability. If unsure, consult a professional welder.
-
Finishing & Testing:
- Surface Preparation: Grind welds smooth, clean all surfaces.
- Corrosion Protection: Apply primer and paint (for steel) or other protective coatings.
- Wiring: Install and connect all lighting and electrical components according to the diagram.
- Mounting: Securely attach the flatbed to the truck chassis, ensuring proper alignment and torque on all bolts.
- Load Testing: Gradually load the flatbed to ensure it performs as expected and that weight distribution is adequate.
Important Considerations & Regulations
Building a flatbed isn’t just about strength; it’s about safety and legality:
- Weight Distribution & GVWR: Ensure the flatbed’s weight, combined with its typical load, does not exceed the truck’s Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) or Gross Axle Weight Ratings (GAWR). Blueprints should guide placement of heavy components.
- Legal Dimensions: Be aware of maximum allowable width, length, and height for vehicles in your region.
- Lighting Standards: All required lighting (tail, brake, turn, marker lights) must be installed correctly and be DOT (Department of Transportation) compliant.
- Frame Compatibility: The flatbed’s mounting system must be compatible with your truck’s specific frame, allowing for chassis flex without inducing stress.
- Safety Features: Incorporate adequate tie-down points, and ensure the headache rack is robust enough to protect the cab.
- Professional Assistance: For complex designs or if you lack fabrication experience, consult a professional engineer or certified welder. Their expertise can prevent costly mistakes and ensure safety.
Common Challenges and Solutions
- Challenge: Excessive Weight.
- Solution: Optimize material selection (e.g., aluminum where possible), use high-strength steel for critical components, and refine structural design to remove unnecessary material.
- Challenge: Rust and Corrosion.
- Solution: Use galvanized steel, aluminum, or apply high-quality primers and paints, including undercoatings. Ensure proper drainage on the deck.
- Challenge: Structural Integrity Issues (Cracks, Bending).
- Solution: Adhere strictly to blueprint specifications, especially concerning crossmember spacing, beam sizes, and welding techniques. Consider professional engineering review for complex designs.
- Challenge: Mounting to the Truck Frame.
- Solution: Research your specific truck’s frame. Use robust, purpose-built mounting brackets that allow for frame flex. Never weld directly to the truck’s frame without specific engineering approval.
- Challenge: Electrical Wiring Problems.
- Solution: Use marine-grade wiring and connectors for durability, ensure proper grounding, and protect wires from abrasion and weather. Follow wiring diagrams meticulously.
Practical Advice and Actionable Insights
- Start Small (If DIY): If you’re new to fabrication, consider building a smaller, simpler project before tackling a full-scale flatbed.
- Safety First, Always: Welding, grinding, and heavy lifting are dangerous. Invest in proper safety gear and understand safe operating procedures.
- Don’t Skimp on Materials for Critical Components: While cost-saving is good, the structural integrity of your flatbed is paramount. Use quality materials for frame rails, crossmembers, and mounting points.
- Plan for the Future: Consider potential future modifications or uses. Adding extra mounting points or pre-drilling for accessories can save time later.
- Consult Professionals: For complex designs, legal compliance, or if you’re unsure about welding, pay for professional engineering or fabrication consultation. It’s an investment in safety and quality.
- Document Everything: Keep a record of your design choices, material purchases, and fabrication steps. This is invaluable for future maintenance or modifications.
Flatbed For Trucks Blueprints: Estimated Price Information
The cost of flatbed blueprints and the subsequent build can vary significantly based on complexity, materials, and whether you DIY or hire professionals. This table provides estimated ranges.
| Category | Description | Estimated Price Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blueprint Acquisition | |||
| Generic/Basic Plans (Online) | Pre-designed, non-customizable plans for common truck sizes. | $50 – $300 | Good starting point for DIYers, but may require adaptation. |
| Custom Blueprint Design (CAD) | Professional design service for bespoke flatbed tailored to specific needs. | $500 – $3,000+ | Varies greatly by designer’s experience, complexity, and included engineering analysis. Highly recommended for unique or heavy-duty applications. |
| Material Costs (Estimated) | (Based on a standard 8ft flatbed for a 3/4 or 1-ton truck. Prices fluctuate based on market, source, and specific grades.) | ||
| Steel Flatbed Materials | Frame, crossmembers, headache rack, decking (steel plate). | $1,000 – $3,500 | Heavier, strong, requires painting. Price depends on steel gauge and market rates. |
| Aluminum Flatbed Materials | Frame, crossmembers, headache rack, decking (aluminum plate). | $2,500 – $6,000+ | Lighter, corrosion-resistant, but more expensive. Welding aluminum is also more specialized. |
| Wood Decking (Separate) | Treated lumber, oak, or composite for the deck surface (if using metal frame). | $200 – $800 | Adds friction, softer on cargo. Can be combined with either steel or aluminum frames. |
| Fabrication Costs (Estimated) | |||
| DIY Fabrication (Tools) | Cost of essential tools (welder, grinder, safety gear, etc.) if you don’t own them. | $500 – $2,500+ | One-time investment. Can be higher for professional-grade equipment. Excludes consumables (welding wire, grinding discs). |
| Professional Fabrication Labor | Cost to hire a certified welder/fabricator to build from your blueprints. | $2,000 – $8,000+ | Highly variable based on shop rates, complexity, and region. Does not include materials. |
| Total Estimated Project Cost | |||
| DIY Build (Materials + Tools) | Building it yourself from purchased blueprints and materials. | $1,700 – $6,300+ | Assumes you acquire basic tools or already own them. |
| Professional Build (All-Inclusive) | Hiring a shop to design and build the flatbed. | $5,000 – $15,000+ | Includes design, materials, and labor. Can go significantly higher for highly specialized or extra-large flatbeds. |
Note: These are estimates and actual costs may vary. Always get multiple quotes for materials and services.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Flatbed For Trucks Blueprints
Q1: Are flatbed blueprints absolutely necessary, or can I just "wing it"?
A1: While some experienced fabricators might attempt a build without formal blueprints, it is highly inadvisable. Blueprints ensure structural integrity, proper dimensions, legal compliance, and safety. "Winging it" significantly increases the risk of structural failure, legal issues, and costly rework.
Q2: Can I build a flatbed myself with blueprints if I have basic welding skills?
A2: Yes, absolutely! Many DIY enthusiasts successfully build flatbeds using detailed blueprints. However, it’s crucial to possess adequate welding and fabrication skills, understand metal properties, and prioritize safety. For critical structural welds, consider having a certified welder inspect or perform them.
Q3: What’s the best material for a flatbed? Steel or Aluminum?
A3: There’s no single "best." Steel is stronger, more affordable, and easier to weld for most DIYers, but it’s heavier and prone to rust. Aluminum is lightweight (better payload, fuel economy) and corrosion-resistant, but more expensive and requires specialized welding skills. Your choice depends on your budget, desired payload, and climate.
Q4: How do I ensure my custom-built flatbed is legal and DOT compliant?
A4: Your blueprints should include all necessary dimensions for legal compliance. Ensure all lighting (tail, brake, turn, marker lights) meets DOT standards. Crucially, your completed flatbed must not exceed your truck’s GVWR or GAWR when loaded. Consult local and state transportation regulations, and consider having a professional inspect your completed build.
Q5: Do flatbed blueprints include wiring diagrams for lights and accessories?
A5: Comprehensive flatbed blueprints often include detailed wiring diagrams for integrated lighting, auxiliary power, and other electrical components. This ensures proper functionality and compliance with vehicle electrical standards.
Q6: How much does it cost to get custom flatbed blueprints designed?
A6: The cost for custom flatbed blueprints from a professional designer can range from $500 to $3,000 or more, depending on the complexity of the design, the level of detail, and any engineering analysis required. Simpler, generic plans can be purchased online for a fraction of that cost.
Q7: Can I modify existing flatbed blueprints to fit my specific truck or needs?
A7: Yes, if you have the necessary design skills (e.g., CAD proficiency) or work with a professional designer. Modifying blueprints allows for fine-tuning dimensions, adding custom features, or adapting them to a different truck chassis while retaining the core structural integrity. However, significant structural changes should always be reviewed by an engineer.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Hauling Potential
Flatbed For Trucks Blueprints are more than just technical drawings; they are the keys to unlocking custom hauling potential, offering unparalleled flexibility, efficiency, and safety. Whether you’re a seasoned fabricator or an individual with a unique hauling challenge, investing in quality blueprints transforms a complex project into a manageable, step-by-step process.
By understanding the components, considering material choices, meticulously following design principles, and adhering to safety and regulatory guidelines, you can create a durable, highly functional flatbed perfectly suited to your needs. Embrace the power of precision planning, and drive forward with a custom solution that truly works for you.