How Many Cubic Yards Of Gravel Can A Triaxle Carry?
How Many Cubic Yards Of Gravel Can A Triaxle Carry? cars.truckstrend.com
Understanding the hauling capacity of heavy machinery is crucial for anyone involved in construction, landscaping, or large-scale material transport. Among the various workhorses of the aggregate world, the triaxle dump truck stands out for its impressive ability to move substantial quantities of material. But precisely how many cubic yards of gravel can a triaxle carry? The answer, while seemingly straightforward, is a complex interplay of truck specifications, material properties, and legal regulations. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of triaxle capacity, providing you with the knowledge needed to plan your projects efficiently, safely, and cost-effectively.
Understanding the Triaxle Dump Truck
How Many Cubic Yards Of Gravel Can A Triaxle Carry?
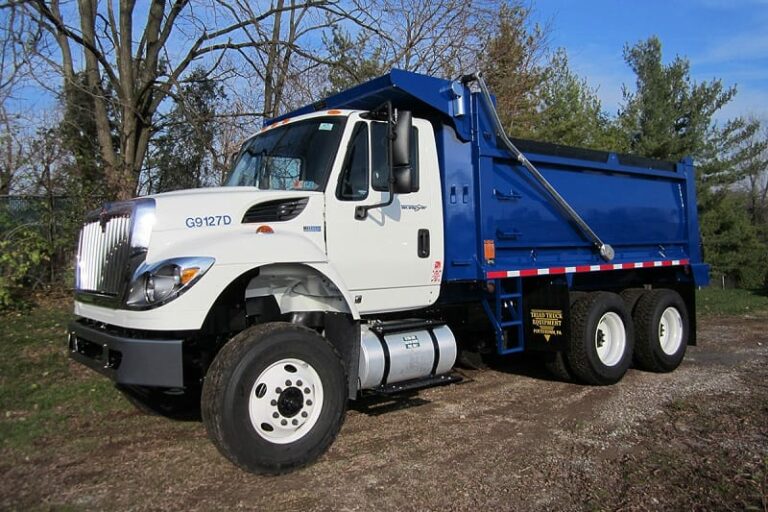
A triaxle dump truck is a heavy-duty commercial vehicle distinguished by its three axles at the rear, in addition to the steer axle(s) at the front. This configuration typically includes two drive axles and one non-drive or "tag" axle (which may be a lift axle) at the rear, allowing for a higher Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) compared to a standard tandem axle truck. The increased number of axles distributes the load more effectively over the road surface, enabling the truck to carry a significantly larger payload while adhering to bridge laws and axle weight limits.
Triaxle trucks are the backbone of many construction and material supply operations due to their versatility and capacity. They are designed to transport heavy, bulk materials such as gravel, sand, asphalt, dirt, and rock. Knowing their precise capacity for a given material like gravel is paramount for several reasons:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Optimizing loads reduces the number of trips, saving fuel, labor, and time.
- Project Planning: Accurate capacity estimates ensure you order the correct amount of material and schedule deliveries effectively, preventing delays or material shortages.
- Legal Compliance: Adhering to weight limits is critical to avoid hefty fines, vehicle damage, and safety hazards.
- Safety: Overloaded trucks are dangerous, affecting braking, steering, and overall stability.
Factors Influencing a Triaxle’s Gravel Capacity
Determining the exact cubic yards a triaxle can carry is not as simple as looking up a single number. Several critical factors come into play, each influencing the practical payload limit.
1. Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) and Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR)
The GVWR is the maximum permissible total weight of the truck, including the vehicle itself, its fuel, passengers, and cargo. For a triaxle dump truck, this typically ranges from 60,000 to 74,000 pounds (30-37 tons), though some specialized configurations can exceed this. The GAWR specifies the maximum weight that can be supported by a single axle or axle group. State and federal regulations dictate these limits to protect roadways and bridges. The truck’s total payload capacity is always constrained by whichever limit is reached first – the overall GVWR or the cumulative GAWR of its axles.
2. Truck Tare Weight (Empty Weight)
The tare weight, or empty weight, of the triaxle truck directly subtracts from its total GVWR to determine the net payload. Tare weights can vary significantly based on the truck’s make, model, engine size, and construction materials. For instance, a truck with an aluminum dump body will be lighter than one with a steel body, allowing it to carry more payload. Typical tare weights for triaxle dump trucks range from 25,000 to 35,000 pounds (12.5-17.5 tons).
3. Density of Gravel
This is perhaps the most crucial factor in converting weight capacity to volume. Gravel, like all aggregates, has varying densities depending on its type, moisture content, and compaction.
- Crushed Stone (e.g., #57, #89): Approximately 2,400 to 2,700 pounds per cubic yard (1.2-1.35 tons/yd³).
- Pea Gravel: Lighter, around 2,000 to 2,500 pounds per cubic yard (1.0-1.25 tons/yd³).
- Bank Run Gravel (unprocessed mix of sand, stone, and clay): Can be heavier, from 2,800 to 3,200 pounds per cubic yard (1.4-1.6 tons/yd³).
- Wet vs. Dry: Wet gravel is always heavier than dry gravel due to the added weight of water. This can significantly reduce the cubic yardage a truck can carry.
It’s important to remember that trucks are limited by weight, not just the volume of their dump bed. A truck’s bed might be able to physically hold 20 cubic yards, but if the material is dense, the truck could hit its weight limit with only 15 cubic yards.
4. State and Local Regulations
Weight limits vary by state and sometimes even by local municipality. Factors like "bridge formulas" (which limit total weight based on axle spacing) and seasonal restrictions (e.g., frost laws in winter/spring that reduce permissible weights to protect thawing roads) can impact how much a triaxle can legally carry. Always consult local Department of Transportation (DOT) guidelines.
Calculating Cubic Yards of Gravel for a Triaxle
To estimate the cubic yards of gravel a triaxle can carry, follow these steps:
-
Determine Net Payload Capacity (in pounds):
- Subtract the truck’s tare weight from its GVWR.
- Example: A triaxle with a GVWR of 74,000 lbs and a tare weight of 30,000 lbs has a net payload capacity of 44,000 lbs (74,000 – 30,000). This translates to 22 tons (44,000 lbs / 2,000 lbs/ton).
-
Obtain the Density of Your Specific Gravel (in pounds per cubic yard):
- If possible, get this from your gravel supplier. Otherwise, use typical ranges.
-
Calculate Cubic Yards:
- Divide the Net Payload Capacity (in pounds) by the Gravel Density (in pounds per cubic yard).
Let’s look at some examples:
Example 1: Standard Crushed Stone (#57)
- Truck Payload: 44,000 lbs (22 tons)
- Gravel Density: 2,600 lbs/cubic yard
- Cubic Yards = 44,000 lbs / 2,600 lbs/yd³ = ~16.9 cubic yards
Example 2: Lighter Pea Gravel
- Truck Payload: 44,000 lbs (22 tons)
- Gravel Density: 2,200 lbs/cubic yard
- Cubic Yards = 44,000 lbs / 2,200 lbs/yd³ = ~20.0 cubic yards
Example 3: Heavier Bank Run Gravel (Wet)
- Truck Payload: 44,000 lbs (22 tons)
- Gravel Density: 3,000 lbs/cubic yard
- Cubic Yards = 44,000 lbs / 3,000 lbs/yd³ = ~14.7 cubic yards
As these examples show, a triaxle can typically carry anywhere from 15 to 20 cubic yards of gravel, depending heavily on the specific type and density of the gravel, and the truck’s exact specifications and legal limits.
Practical Considerations for Hauling Gravel
Beyond the calculations, several practical aspects should be considered when dealing with triaxle gravel deliveries:
- Safety First: Never overload a truck. Overloading compromises braking, steering, and stability, leading to potential accidents, tire blowouts, and damage to the truck and infrastructure. Ensure the load is evenly distributed in the dump body.
- Communication with Supplier: Always communicate the type of truck you are using (e.g., "triaxle dump truck") and the specific type of gravel you need. A good supplier will know the approximate weight per cubic yard of their materials and can help ensure the load is within legal limits.
- Site Accessibility: Ensure your delivery site has adequate space for a triaxle truck to maneuver, dump its load, and exit safely. Consider overhead obstructions (power lines, trees) and ground conditions (soft soil, steep inclines).
- Cost Implications: Knowing the true capacity helps you accurately budget for material and delivery costs. Fewer trips mean lower transportation charges. Always inquire about delivery fees, which can sometimes be as much as the material itself, especially for smaller quantities or longer distances.
- Total Project Volume: For large projects, calculate the total cubic yards of gravel needed and then divide by the estimated triaxle capacity to determine the number of loads required. Factor in a buffer for unexpected needs or minor miscalculations.
Tips for Maximizing Efficiency and Compliance
- Know Your Truck: If you own or operate the triaxle, have it weighed empty at a certified weigh station to know its precise tare weight.
- Verify Regulations: Before embarking on a long haul, especially across state lines, confirm the relevant weight limits and regulations.
- Consider Moisture Content: If purchasing gravel after a heavy rain, be aware that the added water weight will reduce the available cubic yardage for a given legal payload.
- Don’t Guess: When in doubt, always err on the side of caution. An underloaded truck is far better than an overloaded one.
- Leverage Technology: Some weigh stations offer pre-pass systems that allow trucks to bypass the scales if they are within legal limits, saving time.
Estimated Triaxle Gravel Load Cost Table
Please note: Prices for gravel and delivery vary significantly based on geographic location, supplier, quantity ordered, and current market conditions. This table provides estimates for illustrative purposes only. Always obtain a direct quote from your local supplier.
| Gravel Type | Avg. Density (lbs/yd³) | Est. Triaxle Payload (tons) | Est. Triaxle Capacity (yd³) | Avg. Gravel Price/yd³ (Material Only) | Est. Triaxle Load Cost (Material Only) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pea Gravel | 2,200 | 22 | ~20.0 | $35 – $60 | $700 – $1,200 |
| Crushed Stone (#57) | 2,600 | 22 | ~16.9 | $30 – $55 | $507 – $929 |
| Bank Run Gravel | 3,000 | 22 | ~14.7 | $25 – $45 | $367 – $662 |
| Disclaimer | Delivery Fee (Varies Widely) | Typically $75 – $200+ per load |
Material prices are highly variable. Delivery fees are often charged per load and can be a significant portion of the total cost, especially for shorter hauls or smaller quantities. Always get a detailed quote.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How many tons can a triaxle carry?
A triaxle dump truck typically carries between 20 to 25 tons (40,000 to 50,000 pounds) of payload, depending on its tare weight and the specific GVWR allowed by regulations in its operating area.
Q2: Is a triaxle always the best choice for gravel delivery?
Not always. For very small projects (e.g., 1-5 cubic yards), a smaller tandem axle truck or even a pickup truck with a trailer might be more cost-effective due to lower delivery fees. For very large projects requiring hundreds or thousands of cubic yards, transfer trailers or belly dumps (which can carry 25+ cubic yards) might be more efficient. Triaxles hit a sweet spot for medium to large projects.
Q3: How do I know the exact density of my gravel?
The best way is to ask your gravel supplier. They should have data sheets or experience with the specific densities of the materials they sell. If unavailable, use the typical ranges provided in this article, but be conservative.
Q4: What happens if I overload a triaxle truck?
Overloading can lead to several serious consequences:
- Fines: Significant penalties from DOT or law enforcement.
- Safety Hazards: Increased stopping distances, reduced steering control, tire blowouts, and potential rollovers.
- Vehicle Damage: Stress on the drivetrain, suspension, brakes, and frame, leading to costly repairs and reduced lifespan.
- Infrastructure Damage: Excessive weight contributes to premature wear and tear on roads and bridges.
Q5: Can a triaxle carry other materials like sand or dirt?
Yes, triaxle dump trucks are designed to carry a wide range of bulk materials, including sand, dirt, asphalt, and demolition debris. The same principles of weight, density, and legal limits apply to all these materials.
Conclusion
Understanding "how many cubic yards of gravel a triaxle can carry" is more than just a number; it’s a critical aspect of efficient project management, cost control, and safety in the construction and aggregate industries. By factoring in the truck’s specifications (GVWR, tare weight), the material’s density, and relevant legal regulations, you can accurately estimate payload capacity and make informed decisions. Always prioritize safety, communicate clearly with suppliers, and verify local regulations to ensure your operations are compliant and successful. With this knowledge, you can optimize your gravel deliveries, saving time, money, and avoiding potential pitfalls.