What Is The Safest Car Brand? Unveiling the Truth Behind Automotive Safety
What Is The Safest Car Brand? Unveiling the Truth Behind Automotive Safety cars.truckstrend.com
The quest for the "safest car brand" is a fundamental concern for countless car buyers, and for good reason. Our vehicles are not merely modes of transport; they are extensions of our lives, carrying our loved ones, our possessions, and our peace of mind. In an age of increasing traffic density and technological advancement, understanding what truly constitutes automotive safety has become paramount. However, the notion of a single "safest car brand" is largely a misconception. Safety is a complex, multi-faceted attribute determined not by a brand name alone, but by a confluence of rigorous engineering, advanced technology, and continuous innovation applied to specific vehicle models. This comprehensive guide will dissect the elements of car safety, highlight brands that consistently excel, and provide actionable insights for discerning buyers.
Understanding Car Safety: Beyond the Brand Name
What Is The Safest Car Brand? Unveiling the Truth Behind Automotive Safety
The idea that one brand holds an exclusive claim to "safest" is a simplification that overlooks the intricate science and data behind modern automotive safety. While some brands have built a formidable reputation for safety over decades (like Volvo, with its pioneering work in seatbelts and crumple zones), the reality today is that almost all major manufacturers are investing heavily in safety research and development.
True car safety is an evolving target, driven by independent testing agencies and regulatory bodies worldwide. In the United States, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) conducts rigorous crash tests and issues star ratings, while the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) performs its own comprehensive evaluations, including challenging small overlap frontal crash tests and assessing headlight performance. These organizations provide objective, model-specific data that is far more reliable than brand perception alone.
Furthermore, safety is broadly categorized into two critical areas:
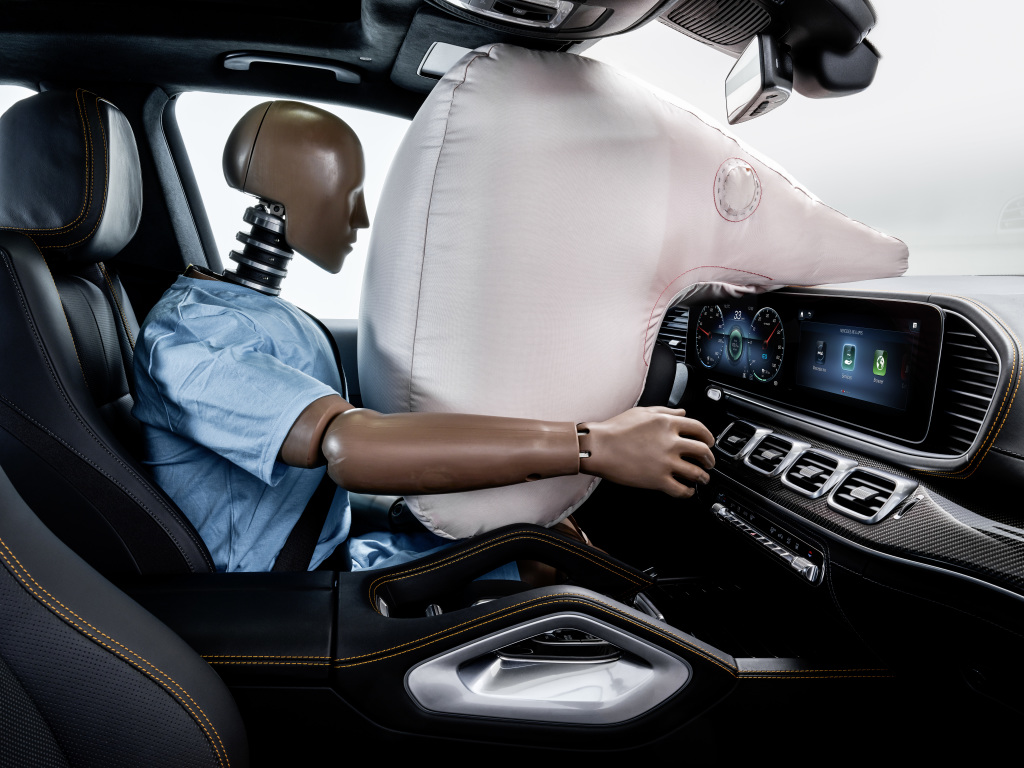
- Passive Safety: Features designed to protect occupants during a crash. These include the vehicle’s structural integrity, airbags, seatbelts, and crumple zones.
- Active Safety: Technologies designed to prevent a crash from happening in the first place. These are often referred to as Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) and include features like automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assist, and blind-spot monitoring.
A truly safe car excels in both active and passive safety measures, and its effectiveness is validated by independent crash test results.
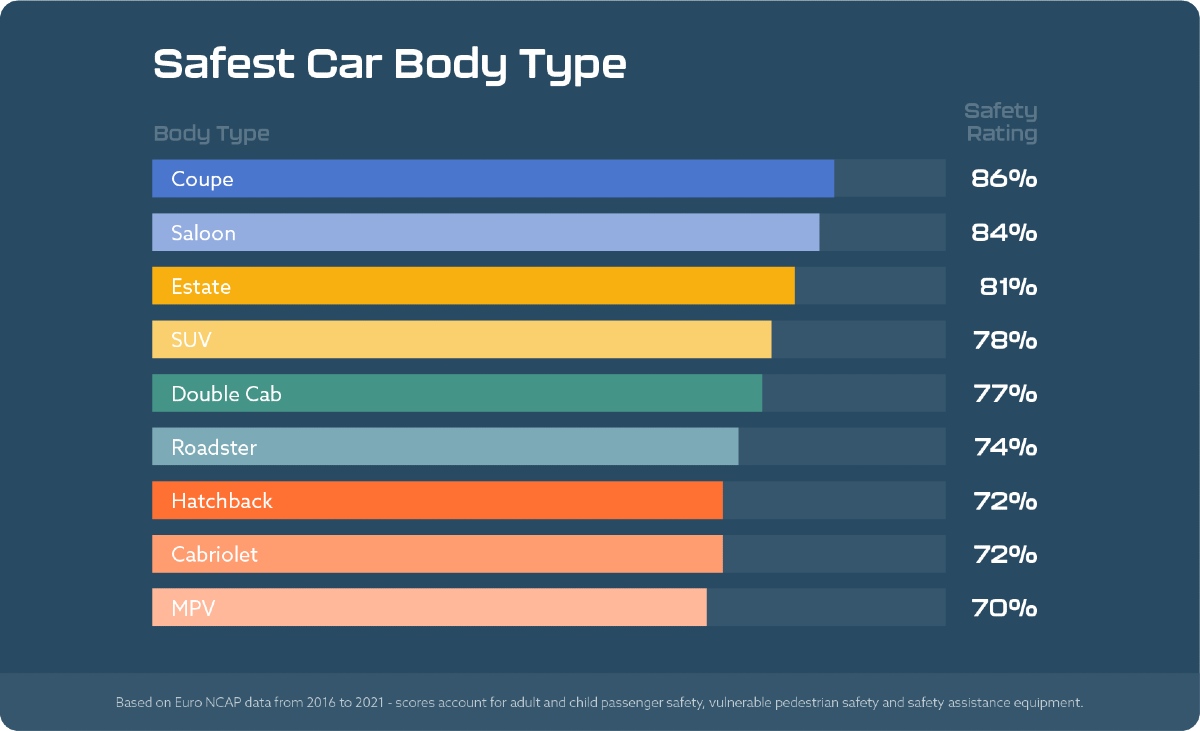
Key Indicators of Car Safety
When evaluating a vehicle’s safety, buyers should look beyond marketing claims and focus on concrete data and features.
Crash Test Ratings
These are the most objective measures of a vehicle’s ability to protect occupants in a collision.
- NHTSA’s 5-Star Safety Ratings Program: Evaluates frontal crash, side crash, and rollover resistance, assigning a star rating (1-5) for each and an overall vehicle score. A 5-star rating indicates the highest level of safety performance.
- IIHS Top Safety Pick and Top Safety Pick+ Awards: The IIHS evaluates vehicles across a broader range of criteria, including:
- Crashworthiness: Moderate overlap front, small overlap front (driver and passenger sides), side impact, roof strength, and head restraints.
- Front Crash Prevention: Assesses the effectiveness of automatic emergency braking systems in vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-pedestrian scenarios.
- Headlights: Rates headlight performance, as poor visibility is a major contributor to nighttime accidents.
- Vehicles earning the "Top Safety Pick+" award achieve the highest ratings in all crashworthiness tests, have advanced or superior ratings for front crash prevention, and acceptable or good ratings for headlights. "Top Safety Pick" vehicles meet similar criteria but may have slightly lower headlight ratings.


Active Safety Features (Preventive)
These technologies actively assist the driver in avoiding accidents. The more comprehensive and well-integrated these systems are, the safer the vehicle.
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): Detects potential frontal collisions with other vehicles or pedestrians and automatically applies the brakes if the driver doesn’t react in time. This is arguably the most impactful active safety feature.
- Lane Departure Warning (LDW) / Lane-Keeping Assist (LKA): LDW alerts the driver if the vehicle drifts out of its lane without signaling, while LKA can gently steer the vehicle back into the lane.
- Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM): Uses sensors to detect vehicles in the driver’s blind spots and alerts the driver, often with a visual warning in the side mirror.
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): Maintains a set speed and a safe following distance from the vehicle ahead, automatically adjusting speed as traffic changes.
- Rear Cross-Traffic Alert (RCTA): Warns the driver of approaching vehicles when backing out of a parking spot or driveway.
- 360-Degree Camera System: Provides a bird’s-eye view of the vehicle’s surroundings, aiding in parking and low-speed maneuvering.
- Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS): Alerts the driver to under-inflated tires, which can affect handling and lead to blowouts.
Passive Safety Features (Protective)
These are the foundational elements that protect occupants during an unavoidable crash.
- Advanced Airbag Systems: Modern vehicles feature multiple airbags (frontal, side curtain, knee, rear side) designed to deploy strategically to cushion occupants from impact.
- Pre-tensioning Seatbelts and Load Limiters: Seatbelts that tighten instantly upon impact to hold occupants securely, then loosen slightly to reduce chest injuries.
- Crumple Zones and Energy-Absorbing Structures: Specifically engineered areas of the vehicle’s frame that deform and absorb crash energy, diverting it away from the passenger compartment.
- High-Strength Steel Construction: The use of advanced materials in critical areas of the vehicle structure to resist deformation and maintain cabin integrity.
- Child Seat Anchors (LATCH system): Standardized attachment points for securely installing child safety seats.
Brands Consistently Ranking High in Safety
While no single brand is "the" safest across its entire lineup, several manufacturers consistently produce models that earn top safety accolades from NHTSA and IIHS, demonstrating a strong commitment to safety across their portfolios.
- Subaru: Often cited for its robust EyeSight driver-assist system, which comes standard or is widely available across its lineup. Subaru models frequently earn IIHS Top Safety Pick+ awards, thanks to strong crashworthiness and effective active safety features. Their symmetrical all-wheel-drive also contributes to stable handling in various conditions.
- Volvo: With a longstanding reputation for safety innovation (they invented the three-point seatbelt), Volvo continues to be a leader. Their "IntelliSafe" suite of safety features is comprehensive, and many of their models consistently achieve top ratings. Volvo’s aspirational goal of zero fatalities or serious injuries in new Volvo cars by 2020 (though not fully met globally due to external factors) underscores their unwavering commitment.
- Mazda: In recent years, Mazda has quietly become a consistent performer in safety. Many of their models, including the Mazda3, CX-5, and CX-9, frequently earn IIHS Top Safety Pick+ awards. Their focus on the "Jinba Ittai" (horse and rider as one) philosophy aims for intuitive driving dynamics that can help drivers avoid accidents.
- Honda/Acura: Honda’s "Honda Sensing" suite and Acura’s "AcuraWatch" offer a comprehensive set of active safety features. Many models from both brands regularly receive high marks from safety organizations, combining strong crash performance with advanced driver assistance.
- Toyota/Lexus: Toyota Safety Sense (TSS) and Lexus Safety System+ (LSS+) are standard on a vast majority of their new vehicles, offering a strong foundation of active safety. Both brands consistently produce models with excellent crash test ratings and high reliability, which indirectly contributes to safety by reducing breakdowns.
- Hyundai/Kia/Genesis: These South Korean brands have made significant strides in safety over the last decade. Their "SmartSense" and similar safety suites are comprehensive, and a growing number of their models across various segments are now routinely earning IIHS Top Safety Pick and Top Safety Pick+ awards, often offering these features at competitive price points.
- Mercedes-Benz/BMW/Audi: Luxury brands often pioneer advanced safety technologies that eventually trickle down to mass-market vehicles. Their robust construction, extensive airbag systems, and sophisticated driver-assistance packages (like Mercedes-Benz’s PRE-SAFE and BMW’s Driving Assistant Professional) contribute to high safety ratings, albeit at a premium price.
It’s crucial to remember that even within these high-ranking brands, safety features and ratings can vary by specific model, trim level, and model year. Always check the individual vehicle you are considering.
Practical Advice for Choosing a Safe Car
Navigating the multitude of safety information can be daunting. Here’s how to make an informed decision:
- Research Specific Models and Years: Do not rely on brand reputation alone. A 2024 Subaru Outback might have a Top Safety Pick+ rating, but a 2010 Subaru Forester might not. Always check the specific year, make, and model you’re interested in on the NHTSA and IIHS websites.
- Prioritize Active Safety Features: While crash protection is vital, preventing the crash altogether is even better. Look for vehicles with a comprehensive suite of active safety technologies like AEB, LDW/LKA, and BSM as standard or widely available options.
- Understand Vehicle Type Considerations:
- SUVs/Trucks: Offer a higher driving position for better visibility but may have a higher center of gravity, increasing rollover risk (though modern stability control systems mitigate this significantly).
- Sedans/Hatchbacks: Often have lower centers of gravity, making them less prone to rollover.
- Size Matters (to a degree): Larger, heavier vehicles generally fare better in collisions with smaller, lighter ones. However, a small car with advanced safety features and good crash ratings can be safer than a large, older vehicle lacking modern safety tech.
- Test Drive and Evaluate Ergonomics: During a test drive, assess visibility (front, rear, and sides), the ease of use of controls, and how intuitive the safety alerts are. A car with great safety features that are distracting or poorly designed can still be unsafe.
- Newer is Generally Safer: Automotive safety technology is constantly evolving. Newer models typically incorporate the latest advancements in structural design, airbag systems, and active safety features. If your budget allows, a newer vehicle often offers superior safety.
- Don’t Skimp on Safety Options: While base models are often more affordable, some crucial active safety features might be optional or only available on higher trims. If safety is your top priority, consider these upgrades.
- Consider Your Driving Habits and Environment: If you frequently drive in heavy traffic, advanced AEB and adaptive cruise control can be invaluable. If you drive in rural areas with wildlife, features like automatic high beams and robust lighting might be more beneficial.
Challenges and Considerations
While the pursuit of the safest car is commendable, there are practical challenges:
- Cost: Advanced safety features and robust vehicle construction often come at a higher price point, especially in premium segments or as part of optional packages.
- Over-reliance on Technology: Driver-assistance systems are aids, not replacements for attentive driving. Over-reliance can lead to complacency and dangerous situations.
- Maintenance and Repair Costs: The sophisticated sensors, cameras, and radar units that power ADAS can be expensive to repair or recalibrate after even minor fender benders.
- Feature Availability: Not all features are available in all markets or on all trim levels, which can complicate the buying process.
- Personal Needs: The "safest" car for a family with young children (e.g., ample space for car seats, rear seat reminders) might differ from the "safest" car for a single commuter (e.g., agile handling for evasive maneuvers).
Safety Feature Availability and Price Considerations Across Vehicle Segments
It’s impossible to put a "price" on safety itself, as it’s an inherent quality and a set of features. However, the table below illustrates how advanced safety features are typically distributed across different vehicle segments and their general impact on price.
| Feature/Rating Metric | Entry-Level Economy Cars (e.g., Toyota Corolla, Hyundai Elantra) | Mid-Range Sedans/SUVs (e.g., Honda CR-V, Mazda CX-5) | Premium/Luxury Vehicles (e.g., Volvo XC60, Mercedes C-Class) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Range (MSRP) | $20,000 – $30,000 | $28,000 – $45,000 | $45,000+ |
| NHTSA 5-Star Rating | Common, often 4 or 5 stars | Very Common, often 5 stars | Very Common, often 5 stars |
| IIHS Top Safety Pick/TSP+ | Possible on higher trims, fewer TSP+ | Very Common, many TSP+ models | Very Common, high percentage of TSP+ models |
| Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) | Often Standard | Standard | Standard (more advanced versions) |
| Lane-Keeping Assist (LKA) | Often Standard | Standard | Standard (more advanced, active steering) |
| Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) | Often Optional/Higher Trim | Standard on most trims | Standard |
| Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) | Often Optional/Higher Trim | Standard on most trims | Standard (often with stop-and-go functionality) |
| Rear Cross-Traffic Alert | Often Optional/Higher Trim | Standard on most trims | Standard |
| 360-Degree Camera | Rare, sometimes on top trim | Optional/Top Trim | Often Standard or widely available |
| Advanced Airbag Systems | Standard (basic) | Standard (more comprehensive) | Standard (most comprehensive, e.g., knee, rear-side) |
| Structural Integrity | Good, designed to meet basic tests | Excellent, designed for various crash scenarios | Exceptional, often leading innovation |
| Headlight Performance | Variable, often just Acceptable | Often Good or Acceptable | Often Good or Superior (adaptive, matrix LED) |
| Overall Safety Value | Good, strong basic safety for the price | Excellent, best balance of features & price | Superior, cutting-edge tech but at a premium |
Note: This table provides general trends. Specific model year, trim level, and manufacturer can cause variations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is there one safest car brand?
A1: No, there isn’t one single "safest car brand." Safety is determined by individual models and their specific features, as validated by independent crash tests from organizations like NHTSA and IIHS. Some brands, like Volvo, Subaru, and Mazda, consistently have a higher percentage of models earning top safety awards.
Q2: Are luxury cars always safer than economy cars?
A2: Not necessarily. While luxury cars often introduce advanced safety technologies first and have robust construction, many economy and mid-range vehicles now offer comprehensive safety suites and achieve top crash test ratings. Always check the specific model’s ratings.
Q3: Do bigger cars mean safer cars?
A3: In a collision between two vehicles of different sizes, the larger, heavier vehicle generally offers more protection. However, a smaller, newer car with advanced safety features and excellent crash ratings can be significantly safer than a larger, older vehicle lacking modern safety technology.
Q4: How do I check a car’s safety rating?
A4: You can check a car’s safety ratings on the official websites of the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA.gov) and the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS.org). Search by specific make, model, and year.
Q5: Are older cars less safe than newer ones?
A5: Generally, yes. Automotive safety technology and engineering have advanced significantly over the past decade. Newer cars benefit from stronger materials, more sophisticated airbag systems, and a wider array of active safety features that were not available in older models.
Q6: What’s the difference between active and passive safety?
A6: Active safety features are designed to prevent a crash from happening (e.g., Automatic Emergency Braking, Lane-Keeping Assist). Passive safety features are designed to protect occupants during a crash (e.g., airbags, seatbelts, crumple zones). Both are crucial for overall vehicle safety.
Conclusion
The pursuit of the "safest car brand" is a noble one, driven by the desire to protect ourselves and our loved ones. However, the answer isn’t a single brand name, but rather a commitment to informed decision-making. True automotive safety is a dynamic interplay of a vehicle’s structural integrity, its advanced active and passive safety features, and its proven performance in rigorous independent crash tests. By focusing on model-specific data from reputable organizations like NHTSA and IIHS, prioritizing comprehensive active safety suites, and understanding the nuances of vehicle design, consumers can confidently choose a car that offers the highest possible level of protection. Ultimately, the safest car is one that combines robust engineering with cutting-edge technology, driven by an alert and responsible driver.





